Distributed control for the optical synchronization system
Maschine Strahlkontrollen
Distributed control for the optical synchronization system
Introduction
The [optical synchronization system](link to LbSync page) at [European XFEL] and [FLASH] provides the necessary < 10fs RMS timing stability and long-term drift-compensation required for many time-resolved experiments conducted with the free-electron lasers, e.g. serial femtosecond crystallography. This is achieved by transporting the reference timing from a central master oscillator to multiple clients within the accelerator facility using optical signals.
The signal flow is represented by a timing distribution tree, where each node represents an RF or laser oscillator and each edge a length-stabilized transmission line. This network of dynamically coupled but locally controlled subsystems needs to be tuned for global performance, for which individual tuning of the local controllers does not suffice. The resulting joint optimization problem is high-dimensional, highly non-convex and subject to multiple constraints, which makes it difficult to solve efficiently.
Furthermore, the high-precision of the timing-synchronization system is achieved with highly sensitive instruments, which have been observed to degrade in performance over time and under the influence of mechanical and electrical stress. Hence, to ensure facility uptime, the control solution should guarantee the performance in view of modeling uncertainties.
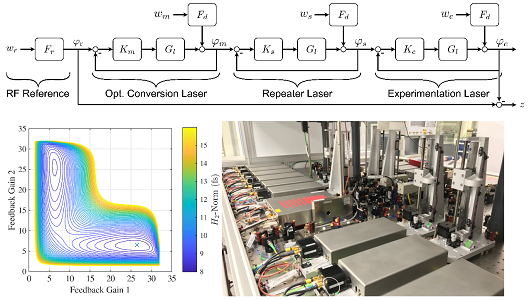
Purpose/goal/objectives:
- Identification and modeling of the dynamics of and disturbances affecting the optical synchronization system at European XFEL and FLASH.
- Performance improvement by structural controller synthesis using mathematical optimization.
- Robustness guarantees against model uncertainties stemming from system aging & degradation.
- Theoretical research on distributed systems, robust H2-optimal control, linear matrix inequalities, integral quadratic constraints, time delay systems and system & phase noise.
References:
- M. Schütte, A. Eichler, H. Schlarb, G. Lichtenberg, H. Werner – “Decentralized Output Feedback Control using Sparsity Invariance with Application to Synchronization at European XFEL” in 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC).
- M. Schütte, A. Eichler, H. Schlarb, G. Lichtenberg, H. Werner - “Convex Synthesis of Robust Distributed Controllers for the Optical Synchronization System at European XFEL” in 2022 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA)
- M. Schütte, A. Eichler, H. Werner – „Structured IQC Synthesis of Robust H2 Controllers in the Frequency Domain” to be published in IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023.